Rather than manually configuring Windows Firewall rules individually on each server, we can instead configure firewall rules for multiple profiles using group policy, allowing us to roll them out to a group of computers at once.
In this example we’ll be working with Windows Server 2016, however the steps are very similar in previous versions of the Windows operating system.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
Configure Firewall Rules Using Group Policy
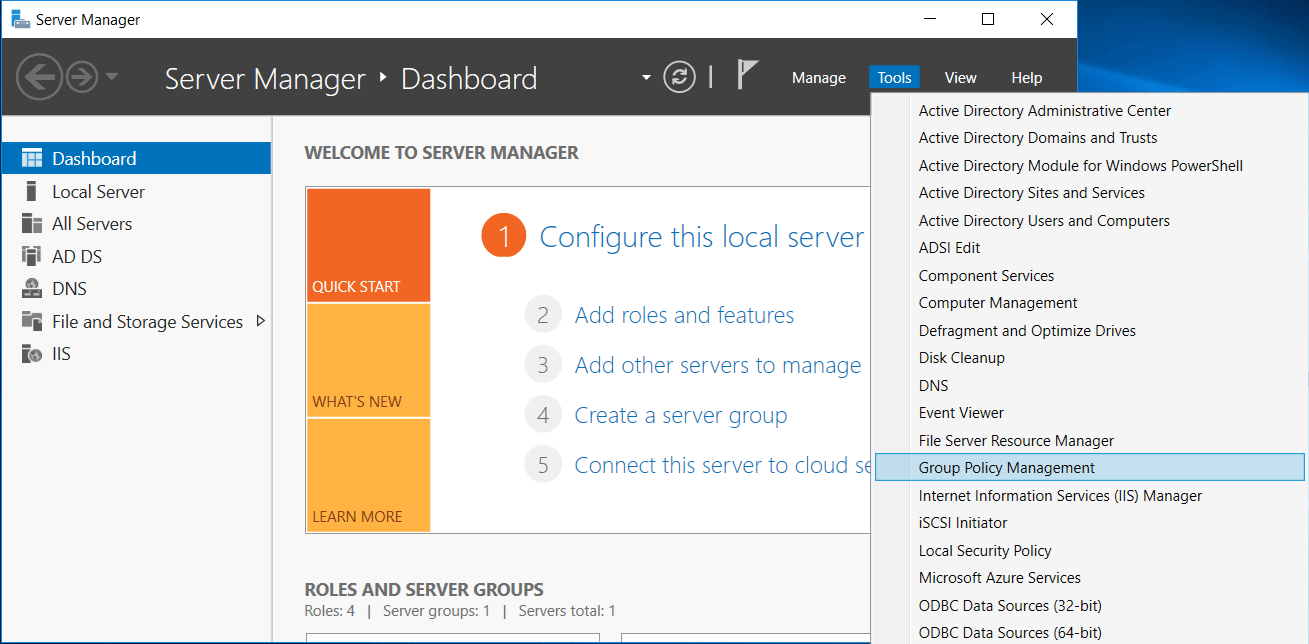
We’ll start by opening Server Manager, selecting Tools, followed by Group Policy Management.
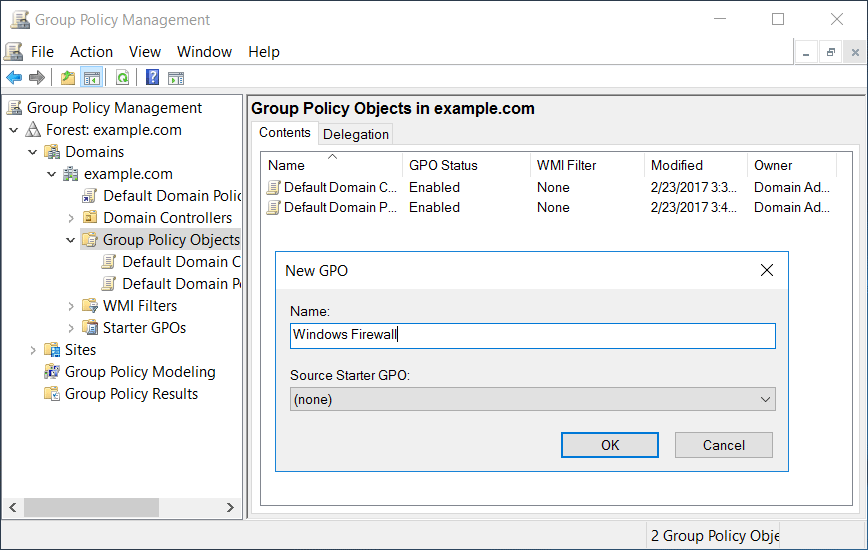
From the Group Policy Management window that opens, we’ll select the group policy objects folder within the domain, right click and select new to create a new group policy object (GPO). In this example we’ll name our GPO “Windows Firewall”.
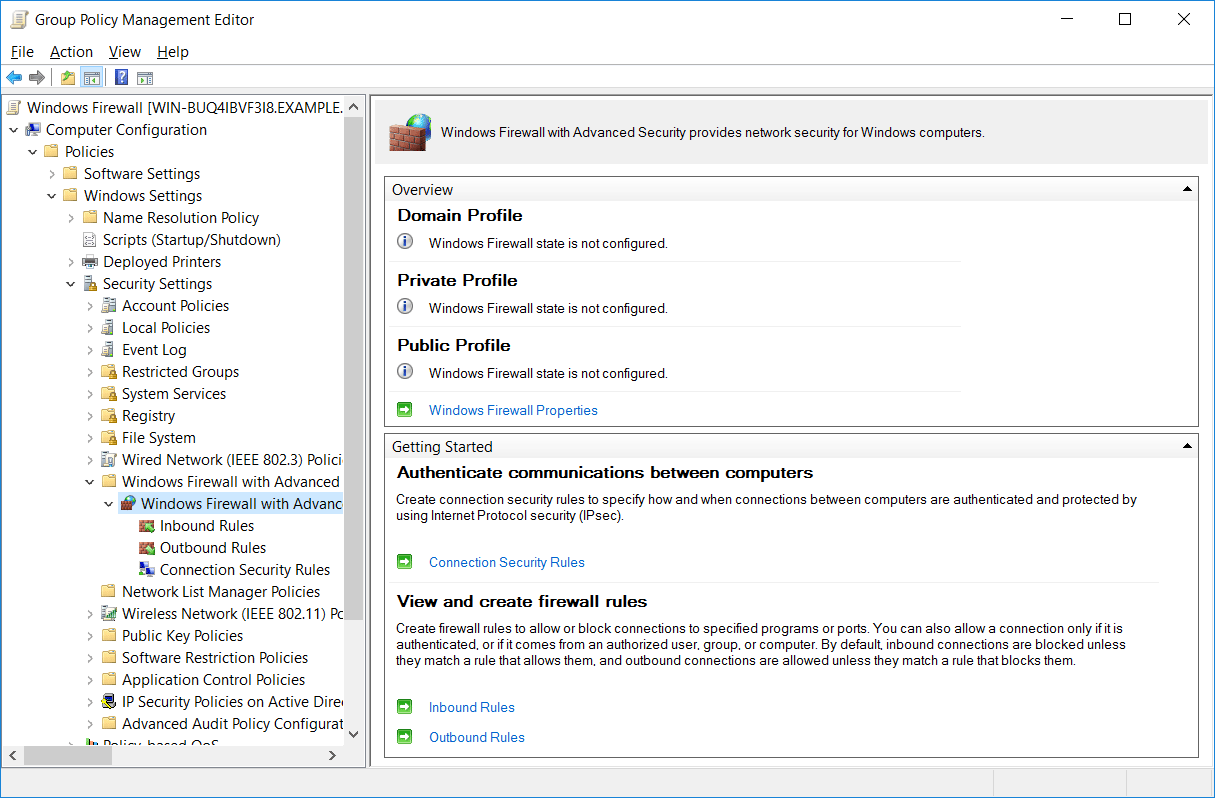
Once the base GPO has been created, right click it and select Edit. This will open the Group Policy Management Editor (GPME). From within GPME, select Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
This interface looks similar to opening up Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on the local system, and configuring it works in much the same way. We can configure inbound, outbound, and connection security rules here simply by selecting one of these options from the options on the left.
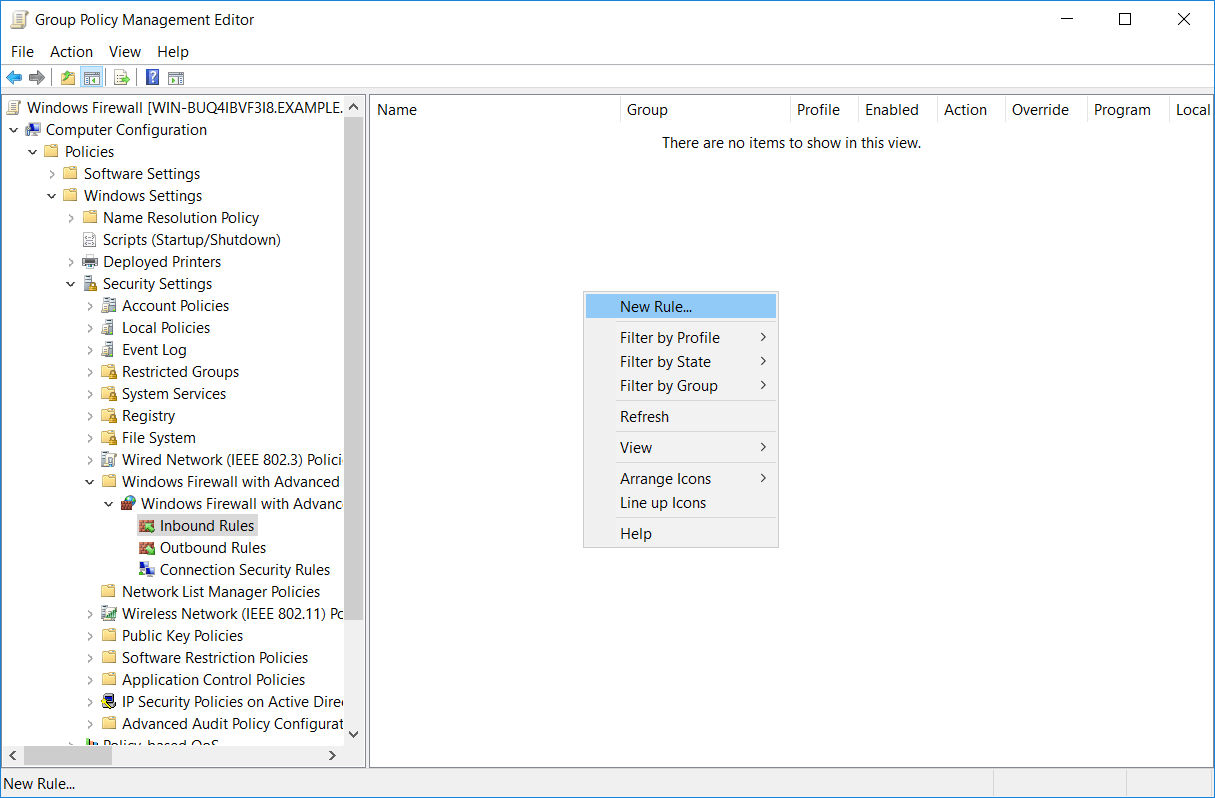
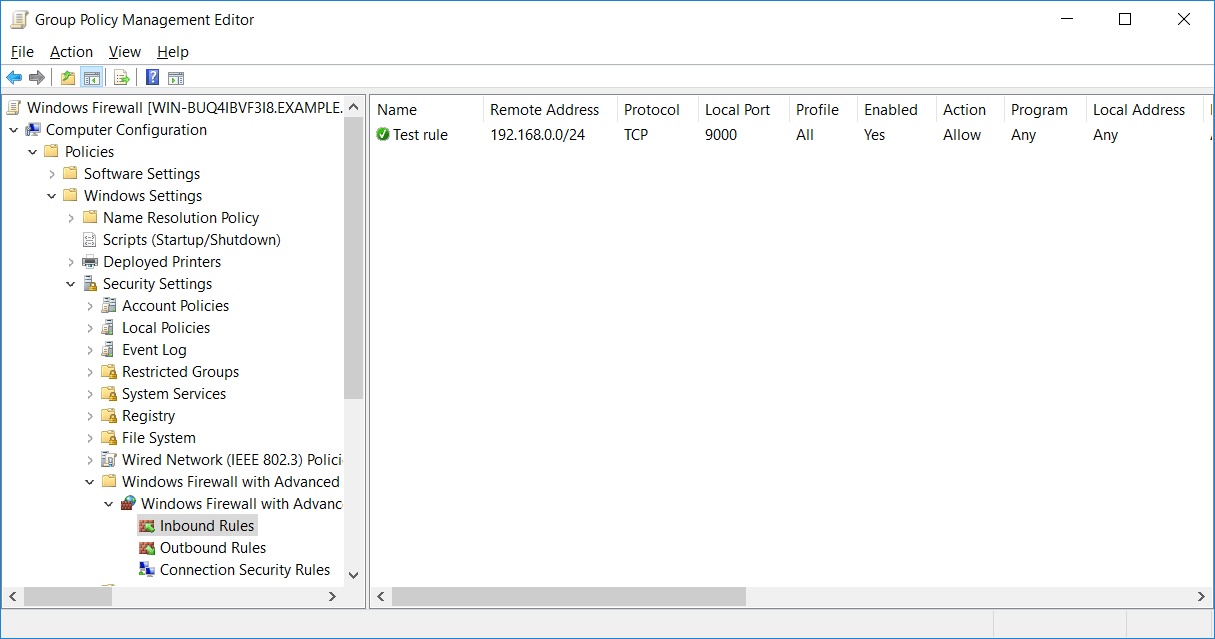
For example if we select inbound rules, we’ll see that there are no rules currently defined as part of this GPO. We can right click and select new rule to create one.
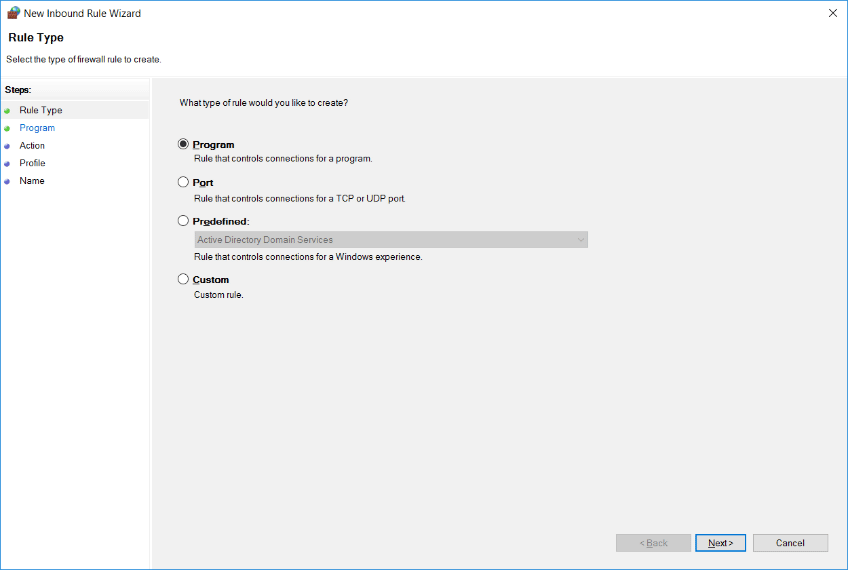
This will then open the new inbound rule wizard, which we covered in our previous post on configuring Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. When creating the rule we specify which profile we want the rule to apply to, whether that be domain, private, or public.
Once the rule has been created we’ll see it listed within the GPO.
At this point we can close the GPME window and apply the GPO to a site, domain, or organizational unit (OU) within Active Directory. In this example I have applied the Windows Firewall GPO to the Domain Controllers container, which contains the computer objects of all domain controllers in the domain, ensuring our custom firewall rules will be automatically rolled out to these machines.
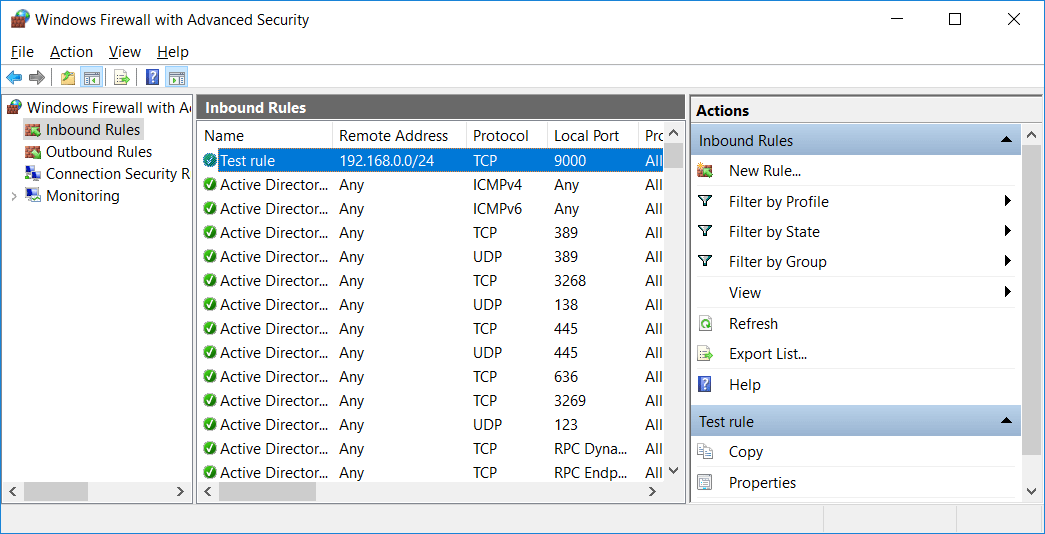
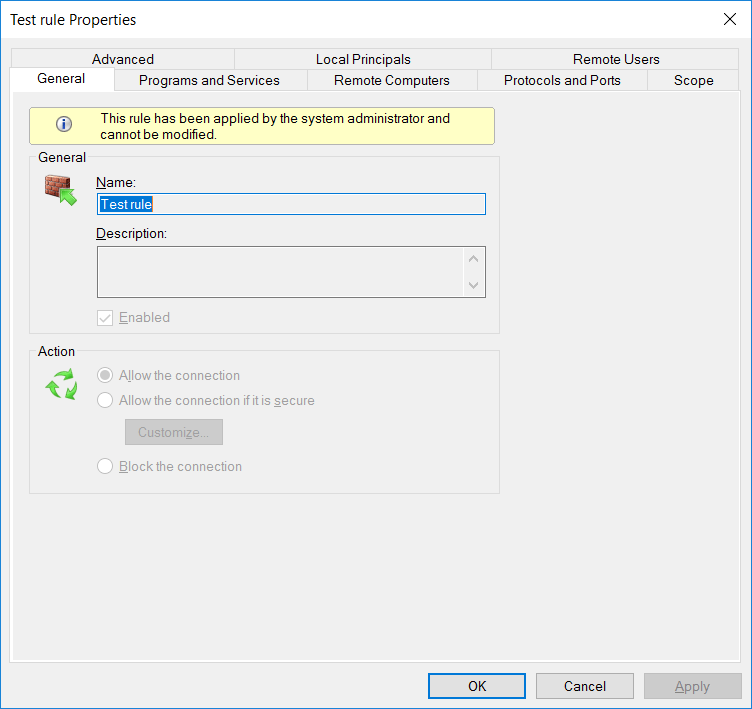
I’ve manually run a ‘gpupdate’ on a domain controller to make the change go out as soon as possible. If I view Windows Firewall with Advanced Security I can see that the rule I created through the GPO is indeed listed.
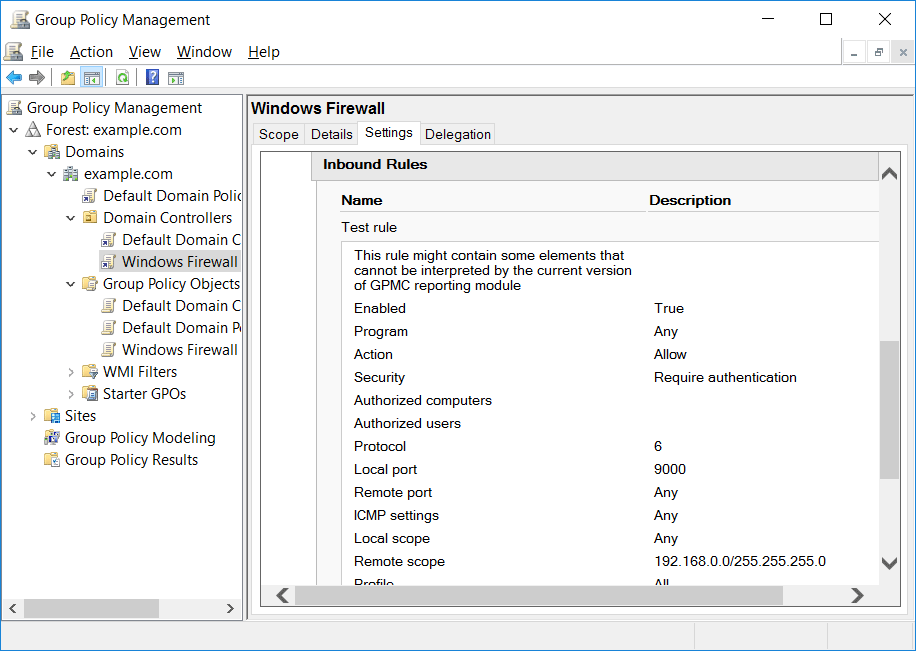
Additionally I am not able to delete the rule here, even as an administrator. If we look at the properties of the firewall rule, we can see up that top that it’s noted that the rule cannot be modified here. This is because it’s being managed through our group policy object.
Import and Export Windows Firewall Settings
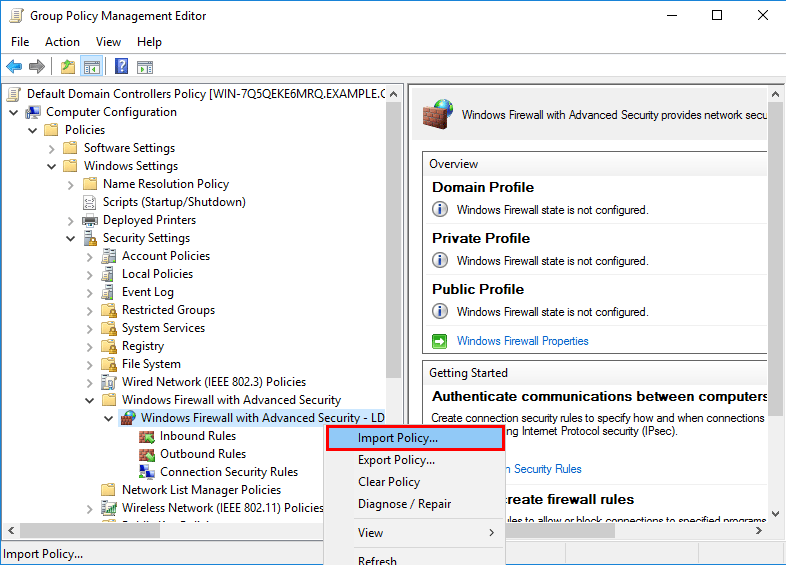
As we covered in our import and export Windows firewall settings post, we can right click the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security root node to import or export the firewall rules. This works the same through the Group Policy Management Editor interface, as shown below we can import rules from a computer and deploy them globally with group policy, or otherwise export the custom rules that we have created within the policy to use elsewhere.
Summary
We can create firewall rules using group policy to apply them to multiple Windows machines from a central location. This also prevents users on the end computers modifying or otherwise removing the firewall rules, as they can only be modified by editing the group policy object.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
0 Comments.