In this post we’ll show you how to configure BitLocker group policy settings. When you enable BitLocker Drive Encryption a number of default settings will be used, such as the strength of the encryption. We can customize these using Group Policy in an Active Directory based domain, allowing us to control the BitLocker settings that get rolled out to all machines in the domain.
In this example we’ll be working with Windows Server 2016, however the steps here are very similar to previous versions of the Windows operating system and should apply there too.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
Configure BitLocker Group Policy Settings
We’ll start by opening Server Manager, selecting Tools, followed by Group Policy Management.
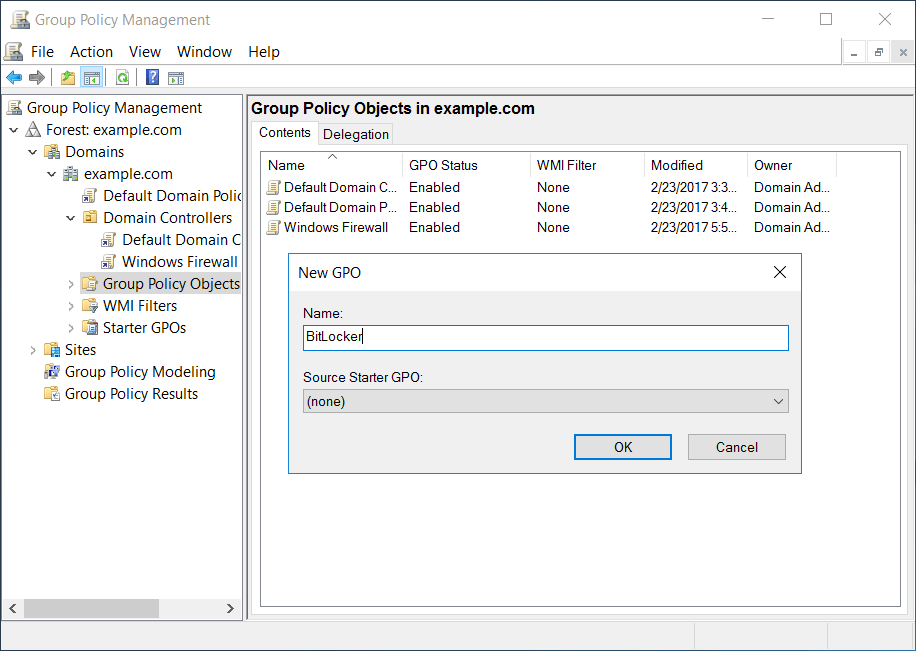
From the Group Policy Management window that opens, we’ll select the group policy objects folder within the domain, right click and select new to create a new group policy object (GPO). In this case we’ll create a new BitLocker GPO for our changes.
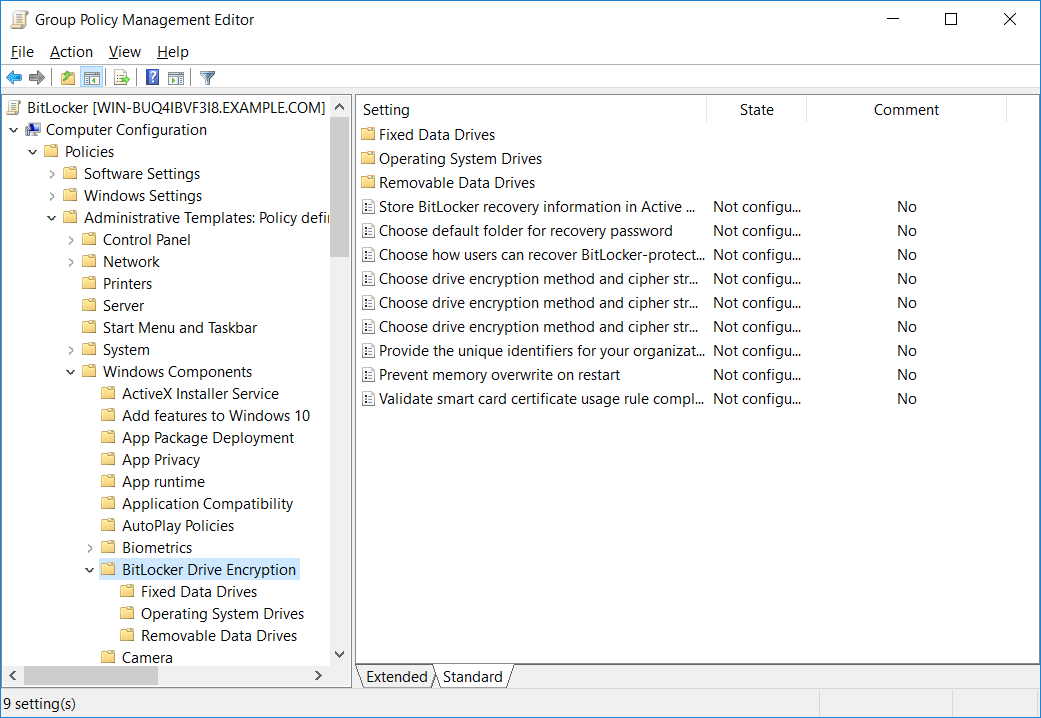
Once the base GPO has been created, right click it and select Edit. This will open the Group Policy Management Editor (GPME). From within GPME, select Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > BitLocker Drive Encryption.
From within here we can set policy for some global BitLocker items, as well as specific policy that applies to the operating system drive, fixed data drives, or removable data drives.
You can now go through the available policies and configure them to meet the requirements of your environment. Some useful policy setting that you may wish to adjust include:
- Store BitLocker recovery information in Active Directory: With this policy enabled it will only be possible to enable BitLocker if an Active Directory domain controller is available so that the recovery key can be stored there. If a domain controller is not available, BitLocker will not enable. This allows you to centrally manage BitLocker recovery keys as they will be stored in Active Directory.
- Choose drive encryption method and cipher strength: By default for Windows 10 this will set XTS-AES 128-bit encryption, this can be modified to XTS-AES 256-bit instead for higher protection.
- Require additional authentication at startup: Rather than only using one authentication method such as TPM, this policy can be enabled to instead require both TPM and a PIN, TPM and a startup key, or TPM with a startup key and PIN.
- Allow enhanced PINs for startup: Enhanced PINs allow you to use additional characters such as uppercase, lowercase, numbers and symbols and should be turned on by default. It allows for stronger PINs to be set.
- Configure minimum PIN length for startup: This allows you to configure the minimum PIN length, which can ensure that your users are forced to set strong BitLocker PINs.
This is not an exhaustive list, but are some of the most commonly modified and useful BitLocker policies. I suggest that you look through all of the available BitLocker policies to get an idea of what you can customize.
At this point we can close the GPME window and apply the GPO to a site, domain, or organizational unit (OU) within Active Directory.
Note: If you make any changes to BitLocker through group policy that you should run a ‘gpupdate’ on the system you wish to deploy BitLocker on so that you can ensure it is fully up to date and has all of your BitLocker policy changes in place. If you already have BitLocker enabled, the settings will not change if you update the policy afterwards, so it’s best to configure BitLocker to meet your requirements through group policy first and then deploy it.
Once enabled, you can view the BitLocker status with the manage-bde command, you should see that the items you’ve applied through Group Policy are listed such as your chosen encryption method.
With these steps you’ll easily be able to configure BitLocker group policy settings centrally from a domain controller.
Summary
As shown we can configure BitLocker group policy settings, allowing us to centrally control the disk encryption options for all Windows machines within our Active Directory domain environment.
This post is part of our Microsoft 70-744 Securing Windows Server 2016 exam study guide series. For more related posts and information check out our full 70-744 study guide.
Thanks for this, after enabling the required GP’s, do we need to configure anything else in order to get the computers to write their keys back to the computer object in AD ?
When I last tested this it just worked after the policy was applied.
Hi Jarrod
Iv enabled the policy’s as instructed, but the drives arent encrypting in my test GPO’s.
Do i need to run a command to kick the encryption off?
If I recall these settings just configure the settings for Bitlocker, you need to actually enable Bitlocker on the machine locally – at least that’s how I did it during device setup when adding to AD and putting the key in AD etc, not sure on the process of automating that part.